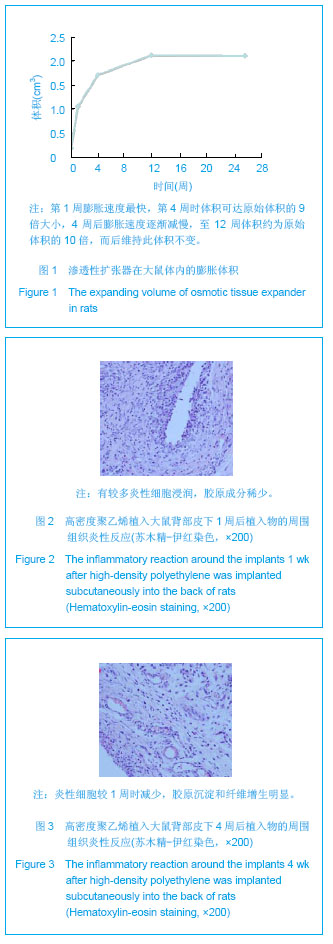
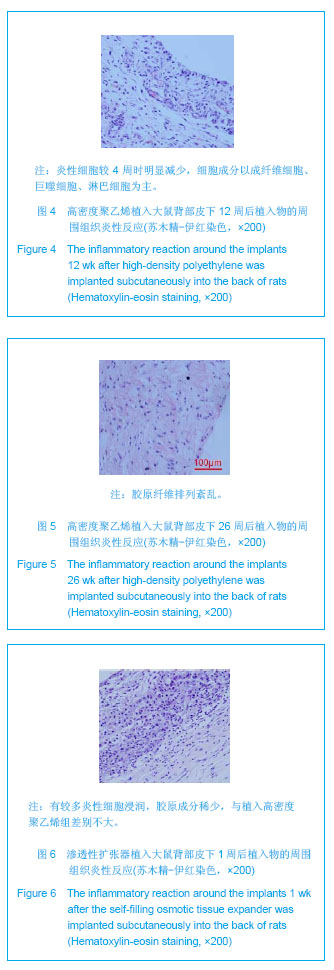
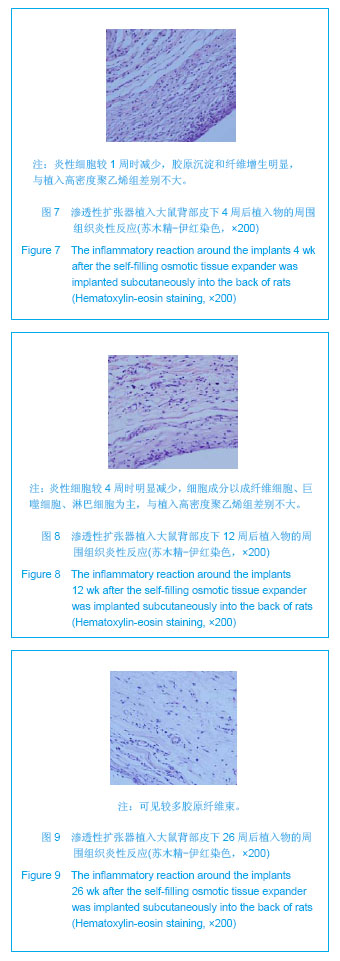
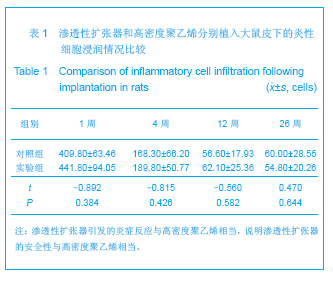
| [1]Fabrizio T.Facial artery flaps in facial oncoplastic reconstruction. Facial Plast Surg.2013;29(5):333-339.[2]Li Y,Xu J,Zhang XZ.Lowering the pivot point of sural neurofasciocutaneous flaps to reconstruct deep electrical burn wounds in the distal foot.Burns.2013;39(4):808-813.[3]Adhikari S,Bandyopadhyay T,Saha JK.Anterior tibial artery perforator plus flaps for reconstruction of post-burn flexion contractures of the knee joint.Ann Burns Fire Disasters.2012; 25(2):86-91.[4]Kayar R.Advancement flaps are enough in most cases as oncoplastic technique for breast cancer even with central or periareolar localization.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst.2013;25(2): 103.[5]Fine NA,Kim JS.Discussion: breast reconstruction modality outcome study: a comparison of expander/implants and free flaps in select patients.Plast Reconstr Surg.2013;131(5): 935-937.[6]Patwardhan S,Shyam AK,Mody RA,et al.Reconstruction of bone defects after osteomyelitis with nonvascularized fibular graft: a retrospective study in twenty-six children.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(9):e561-566, S561.[7]Martin-Smith JD,O'Sullivan JB,Duggan L,et al.Repair of anterior cleft palate fistulae with cancellous bone graft: a simple technique that facilitates dental reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131(3):380e-387e.[8]Sjostrom M,Sennerby L,Lundgren S.Bone graft healing in reconstruction of maxillary atrophy.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2013;15(3):367-379.[9]Gentile P,Di Pasquali C,Bocchini I,et al.Breast reconstruction with autologous fat graft mixed with platelet-rich plasma.Surg Innov. 2013;20(4):370-376.[10]Choi M,Small K,Levovitz C,et al.The volumetric analysis of fat graft survival in breast reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131(2):185-191.[11]陈富禄.皮肤软组织扩张术在烧伤整形外科中的应用探讨[J].吉林医学,2013,34(21):4230-4231. [12]陶卫斌.皮肤软组织扩张术在烧伤整形中的应用[J].中国当代医药,2013,20(13):194-196.[13]Xu K,Li H,Luo Z,et al.Research of pressure of skin soft tissue expander. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2013; 27(3):316-319.[14]Turko A,Fuzaylov G,Savchyn V,et al.Immediate and early tissue expander placement for acute closure of scalp wounds.Ann Plast Surg. 2013;71(2):160-165.[15]Formby P,Flint J,Gordon WT,et al.Use of a continuous external tissue expander in the conversion of a type IIIB fracture to a type IIIA fracture.Orthopedics.2013; 36(2): e249-251.[16]Austad ED,Rose GL.A self-inflating tissue expander.Plast Reconstr Surg.1982;70(5):588-594.[17]Wiese KG,Heinemann DE,Ostermeier D,et al.Biomaterial properties and biocompatibility in cell culture of a novel self-inflating hydrogel tissue expander.J Biomed Mater Res.2001;54(2):179-188.[18]Swan MC,Bucknall DG,Goodacre TE,et al.Synthesis and properties of a novel anisotropic self-inflating hydrogel tissue expander.Acta Biomater.2011;7(3):1126-1132.[19]Radovan C.Breast reconstruction after mastectomy using the temporary expander.Plast Reconstr Surg.1982;69(2): 195-208.[20]Prakash V,Tandon R,Mantri R.Supragaleal placement of tissue expander for post-burn alopecia.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006;59(10):1102-1104.[21]兰久利.皮肤软组织扩张术在烧伤整形外科的应用[J].中国医药指南,2010,8(35):228-229.[22]王国梁,王芳,乔向坤,等.烧伤整形中皮肤软组织扩张术临床治疗体会[J]. 中国医学创新,2013,10(5):127-128.[23]Butler CE,Selber JC.Discussion: the use of acellular dermal matrix in immediate two-stage tissue expander breast reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg.2012;129(5):1059-1060.[24]Hanwright PJ,Davila AA,Mioton LM,et al.A predictive model of risk and outcomes in tissue expander reconstruction: A multivariate analysis of 9786 patients.J Plast Surg Hand Surg.2013.[25]郑大伟,郭杰,马乐,等.皮肤扩张术在头皮缺损修复中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(10):1034-1036.[26]Singh NK,Reaven NL,Funk SE.Cost comparison of immediate one-stage and tissue-expander breast reconstructions after mastectomy in commercially insured patients.Manag Care. 2013;22(3):36-43.[27]鲁开化,郭树忠,艾玉峰,等.皮肤扩张术20年临床应用的回顾[J].中国实用美容整形外科杂志,2005,16(4):209-210.[28]夏来启,陈忠勇,沈运彪,等.皮肤软组织扩张术并发症的分析与防治[J].中国美容医学,2013,22(14):1489-1491.[29]李威扬,宋振涛,简彩,等.皮肤软组织扩张器置入术后感染的治疗与分析[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(15):1917-1919.[30]Brooke S,Mesa J,Uluer M,et al.Complications in tissue expander breast reconstruction: a comparison of AlloDerm,DermaMatrix,and FlexHD acellular inferior pole dermal slings.Ann Plast Surg. 2012;69(4):347-349.[31]Adler N,Dorafshar AH,Bauer BS,et al.Tissue expander infections in pediatric patients: management and outcomes.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124(2):484-489.[32]卢刚,陈光宇,周刚.由扩张器注射壶及导管引发的并发症的分析处理[J].中华整形外科杂志,2000,16(3):17-19.[33]毕国华,刘明宇,陈伟华.皮肤软组织扩张术并发症分析及其防治[J].中国美容医学,2008,17(7):976-978.[34]Bacskulin A,Vogel M,Wiese KG,et al.New osmotically active hydrogel expander for enlargement of the contracted anophthalmic socket. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000; 238(1):24-27.[35]Anwander T,Schneider M,Gloger W,et al.Investigation of the expansion properties of osmotic expanders with and without silicone shell in animals.Plast Reconstr Surg.2007;120(3): 590-595.[36]Gronovich Y,Tuchman I,Binenboym R,et al.Reconstruction with an osmotic tissue expander in pediatric patients.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129(5):863e-865e.[37]Obdeijn MC,Nicolai JP,Werker PM.The osmotic tissue expander: a three-year clinical experience.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62(9):1219-1222.[38]Ronert MA,Hofheinz H,Manassa E,et al.The beginning of a new era in tissue expansion: self-filling osmotic tissue expander--four-year clinical experience.Plast Reconstr Surg.2004;114(5):1025-1031.[39]Sharony Z,Rissin Y,Ullmann Y.Postburn scalp reconstruction using a self-filling osmotic tissue expander.J Burn Care Res. 2009;30(4):744-746.[40]von See C,Rucker M,Bormann KH,et al.Using a novel self-inflating hydrogel expander for intraoral gingival tissue expansion prior to bone augmentation.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2010;48(4):e5-6. |